How to Choose the Right Residential Energy Storage System for Your Needs
In an era where energy independence and sustainability are increasingly prioritized, many homeowners are exploring residential energy storage systems. These systems allow you to store energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar power, ensuring that you have a reliable energy supply even when production is low. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the different types of residential energy storage systems, their benefits, and the factors to consider when choosing the right one for your needs.
Understanding Residential Energy Storage Systems
A residential energy storage system is designed to capture and store electricity for later use, offering a practical solution for homeowners looking to optimize their energy consumption. These systems are typically integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, allowing users to harness and utilize energy more efficiently. By storing excess energy generated during the day, homeowners can effectively manage their energy needs during the night or during peak demand periods when electricity rates are often higher. This capability not only enhances energy independence but also reduces reliance on the grid, contributing to overall cost savings. Moreover, residential energy storage systems provide a backup power source during outages, ensuring that essential appliances remain operational. As the demand for sustainable living increases, these systems are becoming an integral part of modern households, making renewable energy accessible and practical for everyday use.

Types of Residential Energy Storage Systems
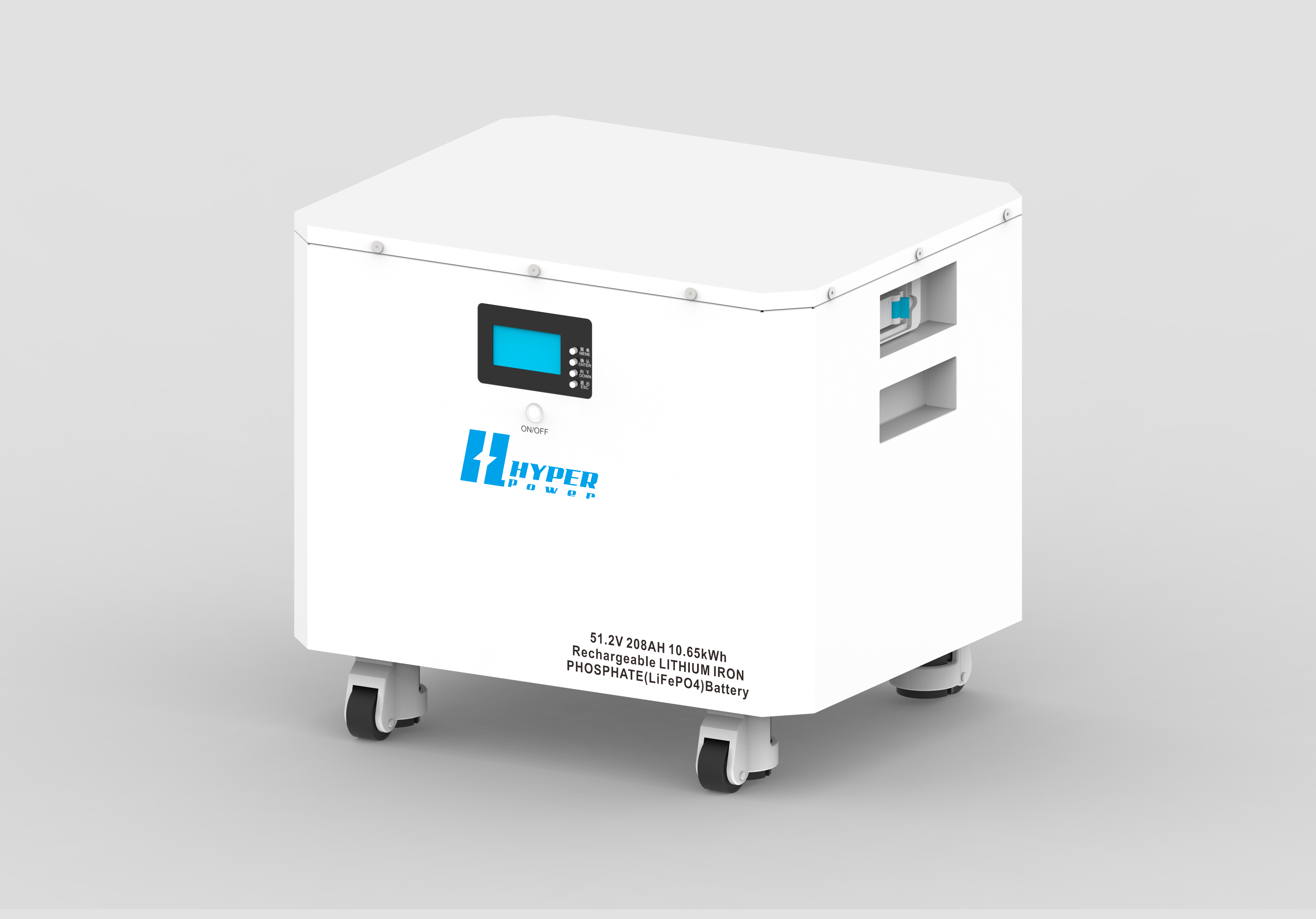
1.Battery Storage Systems
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: The most popular choice for residential energy storage due to their efficiency and longevity. They have a high energy density, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller footprint.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Although cheaper upfront, they have a shorter lifespan and lower efficiency compared to lithium-ion batteries. They are more suited for off-grid applications.
2.Flow Batteries
- Flow batteries use liquid electrolytes to store energy, making them scalable and long-lasting. They are ideal for larger systems but are less common in residential applications due to higher costs.
Saltwater Batteries
- An emerging technology that offers a non-toxic alternative to traditional batteries. While still in development, they promise sustainability and safety.
Pumped Hydro Storage
- This method uses gravitational potential energy to store energy. It is more common in large-scale applications but could be applicable in certain residential setups, particularly in hilly areas.
Key Benefits of Residential Energy Storage Systems
- Energy Independence: By storing energy generated from your solar panels, you can reduce your reliance on the grid, particularly during peak hours when electricity rates are highest.
- Cost Savings: Utilizing stored energy during peak demand periods can significantly lower your electricity bills.
- Backup Power: In the event of a power outage, having a residential energy storage system ensures that you have access to power for essential appliances and devices.
- Environmental Impact: By maximizing the use of renewable energy, residential energy storage systems contribute to reducing your carbon footprint.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Residential Energy Storage System
When selecting the right residential energy storage system for your needs, there are several critical factors to take into account:
1. Energy Needs Assessment
Begin by evaluating your household's energy consumption. Look at your electricity bills to determine your average monthly usage and peak demand times. Consider factors like:
- Total kWh usage per month
- High-consumption appliances (e.g., HVAC systems, electric water heaters)
- Future energy needs (e.g., adding electric vehicles or home expansion)
2. Battery Capacity and Power Rating
Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicating how much energy the system can store. Power rating, measured in kilowatts (kW), indicates how much energy can be drawn from the system at any given time.
- Capacity: Choose a system that can meet your daily energy needs, especially during peak times.
- Power Rating: Ensure the power output is sufficient for your household's maximum demand.
3. Compatibility with Existing Systems
If you already have a solar energy system in place, it’s crucial to ensure that your chosen residential energy storage system is compatible with your existing setup. Many energy storage systems are specifically designed to integrate seamlessly with particular solar inverters, which helps to maximize efficiency and performance. This compatibility allows for optimal energy management, enabling the storage system to effectively capture excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours. By ensuring proper integration, you can enhance the overall functionality of your solar energy system, making the most of your renewable energy investment and improving your household’s energy independence.
4. Budget and Financing Options
Residential energy storage systems can be a significant investment. Consider:
- Upfront Costs: Compare prices of different systems, including installation costs.
- Incentives and Rebates: Research available tax credits, rebates, and financing options that can reduce the overall cost.
- Long-term Savings: Evaluate how much you can save on electricity bills over time versus the initial investment.
5. Warranty and Lifespan
When choosing a residential energy storage system, it's essential to consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer, which typically ranges from 5 to 15 years. A longer warranty often reflects the manufacturer's confidence in the durability and reliability of their product. It suggests that the company stands behind its technology and is willing to cover any potential defects or performance issues over an extended period.
In addition to the warranty, it's crucial to investigate the expected lifespan of the system itself. Most high-quality energy storage systems have a lifespan that can range from 10 to 20 years, depending on factors such as usage patterns, maintenance, and environmental conditions. Understanding both the warranty and the expected lifespan can help you gauge the long-term value of the investment, ensuring that you choose a system that meets your energy needs while providing peace of mind.
6. Installation Requirements
Some systems require professional installation, while others are designed for DIY setups. Consider the following:
- Space Availability: Ensure you have adequate space for the system, including proper ventilation and access.
- Local Regulations: Check local building codes and regulations regarding energy storage systems.
7. Manufacturer Reputation and Support
When selecting a residential energy storage system, it’s vital to research the manufacturer’s reputation thoroughly. Start by examining customer reviews across multiple platforms to gain insights into the experiences of other users. Positive reviews can indicate a reliable product, while consistent complaints about performance or customer service may raise red flags.
Additionally, look for information on the manufacturer’s history and their standing in the industry. A reputable company typically has a proven track record of quality and innovation.
Equally important is assessing the level of customer support and service options they provide. A reliable manufacturer should offer comprehensive support, including installation assistance, troubleshooting, and maintenance services. Look for companies that provide accessible customer service channels, such as phone support, online chat, and extensive FAQs. This level of support ensures that you have help readily available should any issues arise, ultimately contributing to a more satisfactory ownership experience.
8. Monitoring and Control Options
Many modern residential energy storage systems come with monitoring capabilities that allow you to track energy production and consumption in real-time. Consider systems that offer:
- Smartphone apps for easy monitoring
- Integration with home automation systems
Installation and Maintenance of Residential Energy Storage Systems
Installation Process
The installation of a residential energy storage system typically involves the following steps:
- Site Assessment: A professional installer will evaluate your home’s energy needs, existing systems, and suitable locations for the energy storage system.
- System Design: Based on the assessment, a customized system design will be created to meet your specific energy requirements.
- Permits and Approvals: The installer will help navigate any necessary permits and local regulations.
- Installation: The installation process involves mounting the battery, connecting it to the solar system (if applicable), and setting up monitoring systems.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of your residential energy storage system:
- Monitor Performance: Use monitoring tools to track energy output and identify any issues early.
- Inspect Connections: Regularly check electrical connections for wear or damage.
- Clean the System: Keep the battery and surrounding area free from dust and debris to ensure proper ventilation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right residential energy storage system involves careful consideration of your energy needs, budget, and system compatibility. By understanding the different types of systems available and assessing your household's specific requirements, you can make an informed decision that enhances your energy efficiency and independence.
As you explore the benefits of residential solar energy storage systems, remember that investing in these technologies not only offers potential savings but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. Take the time to research and consult with professionals to ensure that your choice aligns with your long-term energy goals.
Blog

Maximizing Energy Independence with Home Lithium Battery Storage

How Residential Photovoltaic Energy Storage Systems Empower Sustainable Homes

Why the 12V Lithium Ion Car Battery is the Smarter Automotive Power Solution — Insights from JEJE Energy









-Charging.png)
.jpg)